Gtk.LockButton¶
Example¶
- Subclasses:
None
Methods¶
- Inherited:
Gtk.Button (29), Gtk.Bin (1), Gtk.Container (35), Gtk.Widget (278), GObject.Object (37), Gtk.Buildable (10), Gtk.Actionable (5), Gtk.Activatable (6)
- Structs:
Gtk.ContainerClass (5), Gtk.WidgetClass (12), GObject.ObjectClass (5)
class |
|
|
Virtual Methods¶
Properties¶
- Inherited:
Gtk.Button (9), Gtk.Container (3), Gtk.Widget (39), Gtk.Actionable (2), Gtk.Activatable (2)
Name |
Type |
Flags |
Short Description |
|---|---|---|---|
r/w |
The |
||
r/w/c |
The text to display when prompting the user to lock |
||
r/w/c |
The text to display when prompting the user to unlock |
||
r/w/c |
The tooltip to display when prompting the user to lock |
||
r/w/c |
The tooltip to display when prompting the user cannot obtain authorization |
||
r/w/c |
The tooltip to display when prompting the user to unlock |
Style Properties¶
- Inherited:
Signals¶
- Inherited:
Gtk.Button (6), Gtk.Container (4), Gtk.Widget (69), GObject.Object (1)
Fields¶
- Inherited:
Gtk.Button (6), Gtk.Container (4), Gtk.Widget (69), GObject.Object (1)
Name |
Type |
Access |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
parent |
r |
Class Details¶
- class Gtk.LockButton(*args, **kwargs)¶
- Bases:
- Abstract:
No
- Structure:
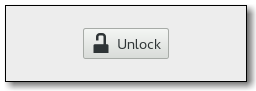
Gtk.LockButtonis a widget that can be used in control panels or preference dialogs to allow users to obtain and revoke authorizations needed to operate the controls. The required authorization is represented by aGio.Permissionobject. Concrete implementations ofGio.Permissionmay use PolicyKit or some other authorization framework. To obtain a PolicyKit-basedGio.Permission, use polkit_permission_new().If the user is not currently allowed to perform the action, but can obtain the permission, the widget looks like this:
and the user can click the button to request the permission. Depending on the platform, this may pop up an authentication dialog or ask the user to authenticate in some other way. Once the user has obtained the permission, the widget changes to this:
and the permission can be dropped again by clicking the button. If the user is not able to obtain the permission at all, the widget looks like this:
If the user has the permission and cannot drop it, the button is hidden.
The text (and tooltips) that are shown in the various cases can be adjusted with the
Gtk.LockButton:text-lock,Gtk.LockButton:text-unlock,Gtk.LockButton:tooltip-lock,Gtk.LockButton:tooltip-unlockandGtk.LockButton:tooltip-not-authorizedproperties.- classmethod new(permission)[source]¶
- Parameters:
permission (
Gio.PermissionorNone) – aGio.Permission- Returns:
a new
Gtk.LockButton- Return type:
Creates a new lock button which reflects the permission.
New in version 3.2.
- get_permission()[source]¶
- Returns:
the
Gio.Permissionof self- Return type:
Obtains the
Gio.Permissionobject that controls self.New in version 3.2.
- set_permission(permission)[source]¶
- Parameters:
permission (
Gio.PermissionorNone) – aGio.Permissionobject, orNone
Sets the
Gio.Permissionobject that controls self.New in version 3.2.
Property Details¶
- Gtk.LockButton.props.permission¶
- Name:
permission- Type:
- Default Value:
- Flags:
The
Gio.Permissionobject controlling this button
- Gtk.LockButton.props.text_lock¶
-
The text to display when prompting the user to lock
- Gtk.LockButton.props.text_unlock¶
-
The text to display when prompting the user to unlock
- Gtk.LockButton.props.tooltip_lock¶
- Name:
tooltip-lock- Type:
- Default Value:
'Dialog is unlocked.\nClick to prevent further changes'- Flags:
The tooltip to display when prompting the user to lock
- Gtk.LockButton.props.tooltip_not_authorized¶
- Name:
tooltip-not-authorized- Type:
- Default Value:
'System policy prevents changes.\nContact your system administrator'- Flags:
The tooltip to display when prompting the user cannot obtain authorization